Mounjaro, a weight loss medication used to treat type 2 diabetes and chronic weight management. Like all weight loss medications, it comes with its own set of potential side effects. Understanding these side effects and knowing how to manage them can significantly improve your experience and adherence to the treatment.
In this blog you’ll learn about the common side effects of Mounjaro and practical tips on how to minimise them with diet and lifestyle changes.
What is Mounjaro?
Mounjaro is used to treat obesity and is administered weekly through an injection. It contains an active ingredient called Tirzepatide, which helps regulate appetite and glucose levels. The primary mechanism of Mounjaro involves mimicking the effects of natural hormones in the body that control blood sugar and hunger. By doing so, it helps reduce food intake and promote a feeling of fullness.
Mounjaro is prescribed for patients with a BMI over 30 (obese) and for those with a BMI over 27 (overweight) who have weight-related health issues like prediabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or heart problems. It is often used in combination with a comprehensive weight management programme that includes dietary changes, increased physical activity, and behavioural therapy.
Common Side Effects of Mounjaro
While Mounjaro is generally well-tolerated, some patients may experience side effects. Here are some of the most common ones:
Nausea and Vomiting
One of the most frequently reported side effects of Mounjaro is nausea. It is generally mild and should go away after the first two weeks.
Nausea can sometimes lead to vomiting, especially during the initial stages of treatment as the body adjusts to the medication.
Management Tips:
- Take Mounjaro with food to help reduce nausea.
- Stay hydrated by sipping water throughout the day.
- Eat small, frequent meals instead of large ones.
Headaches
Headaches are another common side effect experienced by Mounjaro users. These headaches can range from mild to severe and may occur sporadically.
Management Tips:
- Ensure you’re drinking enough water, as dehydration can exacerbate headaches.
- Rest in a quiet, dark room if a headache occurs.
- Over-the-counter pain relief medications can be helpful, but consult your GP first.
Dizziness
Dizziness is a side effect that some users report, particularly when they first start taking Mounjaro. This can be unsettling and may affect daily activities.
Management Tips:
- Stand up slowly from sitting or lying positions to avoid sudden dizziness.
- Avoid driving or operating heavy machinery if you feel dizzy.
- Ensure you’re eating enough throughout the day to maintain blood sugar levels.
Fatigue
Feeling fatigued or unusually tired is another side effect that some individuals may experience while on Mounjaro. This can impact productivity and overall quality of life.
Management Tips:
- Get plenty of rest and prioritise sleep.
- Engage in light physical activity to boost energy levels.
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in nutrients.
Dry Mouth
A common but less severe side effect is dry mouth. It can be uncomfortable but is generally manageable with some simple strategies.
Management Tips:
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Chew sugar-free gum or suck on sugar-free sweets to stimulate saliva production.
- Avoid caffeine and alcohol, which can worsen dry mouth.
Constipation
Constipation is another side effect that some Mounjaro users encounter. It can be uncomfortable and lead to other digestive issues.
Management Tips:
- Increase your fibre intake by eating fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Drink plenty of water to help move food through your digestive system.
- Engage in regular physical activity to promote bowel movements.
Diarrhoea
Conversely, some individuals may experience diarrhoea while taking Mounjaro. This can lead to dehydration and discomfort if not managed properly.
Management Tips:
- Stay hydrated by drinking water and electrolyte solutions.
- Avoid fatty, spicy, or high-fibre foods that can exacerbate diarrhoea.
- Consult your doctor if diarrhoea persists or becomes severe.
Insomnia
Some users report insomnia or difficulty sleeping when taking Mounjaro. This can affect overall health and well-being if not addressed.
Management Tips:
- Establish a regular sleep routine with consistent bedtimes and wake-up times.
- Avoid caffeine and other stimulants, especially in the afternoon and evening.
- Create a relaxing bedtime environment and practice good sleep hygiene.
Increased Heart Rate
An increased heart rate is a less common but notable side effect of Mounjaro. This can be concerning, especially for individuals with preexisting heart conditions.
Management Tips:
- Monitor your heart rate regularly.
- Avoid strenuous activities that can excessively raise your heart rate.
- Consult your healthcare provider if you notice significant changes in your heart rate.
Mood Changes
Some individuals may experience mood changes while taking Mounjaro. These can include irritability, anxiety, or even depressive symptoms.
Management Tips:
- Practice stress-relief techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Maintain open communication with friends and family about your feelings.
- Seek professional help if mood changes become severe or unmanageable.
Side Effects Based on Mounjaro Dosage Escalation
While Mounjaro is generally well tolerated, different dosages can lead to varying rates of side effects. The SURMOUNT-1 clinical trial assessed the safety of Tirzepatide in adults with obesity or who were overweight but did not have diabetes. The most commonly reported side effects were related to the gastrointestinal system, particularly during dose increases. Fortunately, these side effects typically improve with continued use.
Here’s what the trial found:
For those on a 5 mg dose of tirzepatide:
- 24.6% experienced nausea
- 18.7% experienced diarrhoea
- 16.8% experienced constipation
- 8.3% experienced vomiting
For those on a 10 mg dose:
- 33.3% experienced nausea
- 21.2% experienced diarrhoea
- 17.1% experienced constipation
- 10.7% experienced vomiting
For those on a 15 mg dose:
- 31.0% experienced nausea
- 23.0% experienced diarrhoea
- 11.7% experienced constipation
- 12.2% experienced vomiting
In comparison, those on a placebo reported:
- 9.5% experienced nausea
- 7.3% experienced diarrhoea
- 5.8% experienced constipation
- 1.7% experienced vomiting
These side effects are crucial to consider when deciding on a treatment plan. Mounjaro may not be suitable for everyone, so it’s important to discuss the options with your healthcare provider to determine the best course of action for you.
Serious Side Effects of Mounjaro
Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is a potentially life-threatening condition characterised by inflammation of the pancreas. Symptoms include severe abdominal pain, vomiting, and fever. If you experience these symptoms, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention.
Thyroid Tumours
There have been reports of thyroid tumours, including cancer, in patients taking Mounjaro. Symptoms may include a lump in the neck, difficulty swallowing, or shortness of breath. Regular monitoring and communication with your healthcare provider are essential to mitigate this risk.
Hypoglycaemia
While Mounjaro helps control blood sugar levels, it can also cause them to drop too low, leading to hypoglycaemia. Symptoms of hypoglycaemia include dizziness, sweating, confusion, and even loss of consciousness. Patients should monitor their blood sugar levels regularly and be aware of the signs of hypoglycaemia.
Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions to Mounjaro can be severe and may include symptoms such as rash, itching, swelling, severe dizziness, and trouble breathing. Anaphylaxis, a potentially life-threatening allergic reaction, requires immediate medical intervention.
Kidney Problems
Mounjaro can cause kidney problems, particularly in patients with pre-existing kidney conditions. Symptoms of kidney issues include changes in urine output, swelling in the legs and ankles, and fatigue. Regular kidney function tests are recommended for patients on Mounjaro.
Heart Problems
Cardiovascular diseases, such as heart attack and stroke, have been reported in some patients taking Mounjaro. Symptoms of a heart attack may include chest pain, shortness of breath, and nausea. Symptoms of a stroke include sudden numbness, confusion, and difficulty speaking or understanding speech. Immediate medical attention is crucial if these symptoms occur.
How to Minimise the Risk of Mounjaro Side Effects?
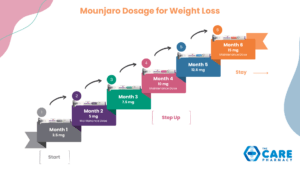
To minimise the risk of side effects, you should start Mounjaro with a lower dose of 2.5 mg per week. After 4 weeks, the dose is increased to 5 mg. Further increases in dosage might occur based on how well the medication is tolerated. Typically, the dose is raised by 2.5 mg increments every 4 weeks until reaching a maximum of 15 mg per week.
If you are unable to tolerate a dose well, it is recommended to remain at the current dose for a longer period before increasing further or even to decrease the dose. However, most of the side effects can be managed with dietary and lifestyle changes.
When Should You Seek Professional Help?
Although most of the common side effects of Mounjaro can be managed through diet and lifestyle changes. You should fill an online consultation form if you’re experiencing any of the above mentioned Mounjaro side effects. Our healthcare provider at The Care Pharmacy can help patients navigate these potential side effects and determine the proper course of weight management treatments.
FAQs
How long do Mounjaro side effects last?
The duration of side effects from Mounjaro (Tirzepatide) can vary depending on the individual, the specific side effect, and the duration of treatment. Generally, some common side effects may last for a few days to a couple of weeks as the body adjusts to the medication.
How to minimise Mounjaro side effects?
To minimise Mounjaro side effects, start with a lower dose and gradually increase it as directed by your doctor. Eating smaller, more frequent meals and avoiding high-fat foods can help reduce nausea. Staying hydrated and following a consistent injection schedule can also help manage side effects.
How do you treat injection side reactions with Mounjaro?
Injection site reactions with Mounjaro are usually mild and tend to go away on their own. If you experience a reaction at the injection site, using an ice pack on the area after your injection can help reduce pain and swelling. To avoid injection site reactions, try changing the spot where you inject the drug each time.
How long does Mounjaro stay in your system?
Mounjaro has a half-life of about 5 days, meaning it takes approximately 5 days for half of the drug to be eliminated from your body. It can take around 25-30 days (or roughly 5 half-lives) for Mounjaro to be fully cleared from your system.
How to get Mounjaro out of your system fast?
There is no way to quickly remove Mounjaro from your system, as the body needs time to naturally metabolise and eliminate the drug. Stopping Mounjaro means any side effects you experienced will also cease.
Medically reviewed by
Mohammed Lakhi
Superintendent Pharmacist












